Circuit Theory

Circuit theory
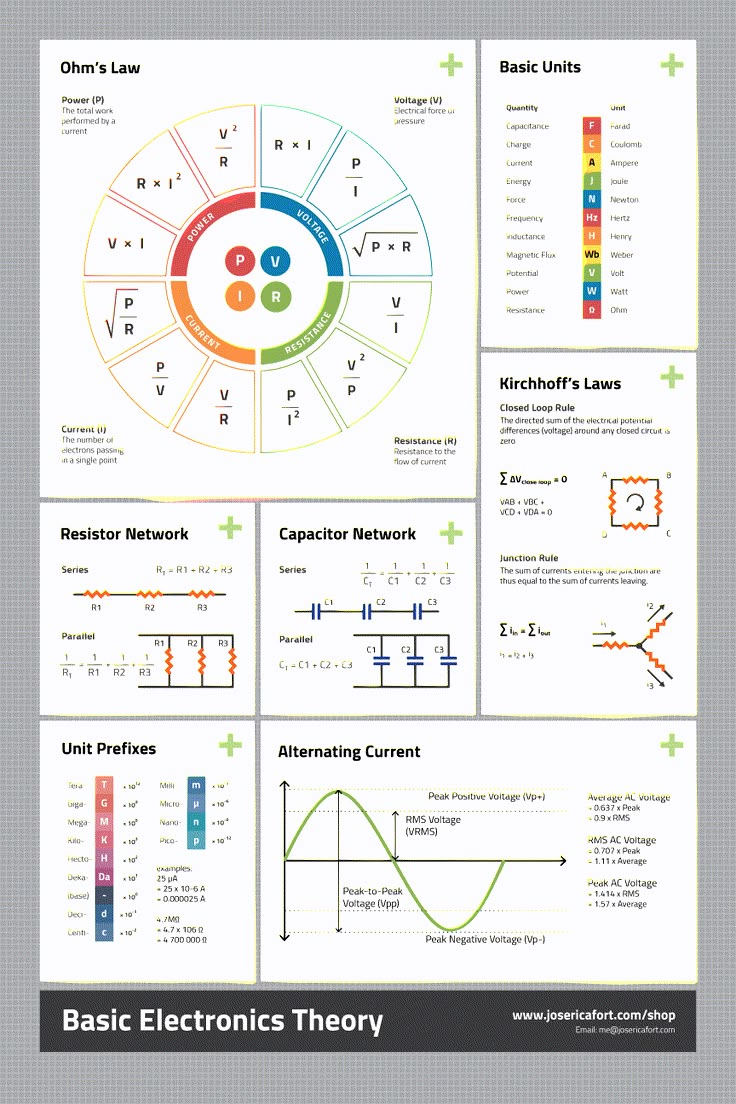
A cornerstone of circuit theory is Ohm's law, which is a simple formula for working out the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. The formula is written as "current equals voltage divided by resistance." In other words, the resistance of a conductor is independent of the current.
What is the importance of circuit theory?
Circuit theory is also valuable to students specializing in other branches of the physical sciences because circuits are a good model for the study of energy systems in general, and because of the applied mathematics, physics, and topology involved.
What is DC circuit theory?
Advertisement. Basic DC circuit theory looks at how an electric circuit is an interconnection of electrical elements and that electrical current is the flow of charge, measured in amperes (A) being pushed around a closed circuit by a potential difference (electromotive force) known as voltage, measured in volts (V).
What is the easiest way to learn circuit theory?
Follow these steps:
- Get a standard textbook like Electric Circuits by Sadiku.
- Spend some Rs 500/- and buy these : a breadboard, resistances, some LEDs, 9V battery, wires and multimeter.
- Start reading the textbook. Start from the very basic like Ohms Law.
- Try to implement what you studied on the breadboard.
What are the 3 circuit laws?
From this definition, three rules of series circuits follow: all components share the same current; resistances add to equal a larger, total resistance; and voltage drops add to equal a larger, total voltage.
What are the 5 elements of a circuit?
The following common components are used in most printed circuit boards:
- Resistors. Resistors control the electric currents that pass through them, as well as the voltage in each component connected to them.
- Transistors. ...
- Capacitors. ...
- Inductors. ...
- Diodes.
What are the limitations of circuit theory?
The limitations of circuit models come into play as the frequency is raised so high that the propagation time of electromagnetic fields becomes comparable to a period, with the result that "inductors" behave as "capacitors" and vice versa. Other limitations are associated with loss phenomena.
Who invented circuit theory law?
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. They were first described in 1845 by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff.
What is circuit explain?
In electronics, a circuit is a complete circular path that electricity flows through. A simple circuit consists of a current source, conductors and a load. The term circuit can be used in a general sense to refer to any fixed path that electricity, data or a signal can travel through.
What is AC and DC theory?
There are two types of current, direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). DC is current that flows in one direction with a constant voltage polarity while AC is current that changes direction periodically along with its voltage polarity.
What is AC and DC circuit?
Electric current flows in two ways as an alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). In alternating current, the current keeps switching directions periodically – forward and backward. While in the direct current it flows in a single direction steadily.
Why Wheatstone bridge is DC?
Wheatstone's bridge is a simple DC bridge, which is mainly having four arms. These four arms form a rhombus or square shape and each arm consists of one resistor. To find the value of unknown resistance, we need the galvanometer and DC voltage source.
What are the rules for circuit diagrams?
When drawing circuit diagrams, there are a few important rules to remember:
- Cables and wires in a circuit are drawn as straight lines.
- Wires should not cross over each other.
- We need to use the correct symbols for each component in the circuit.
- When drawn, the circuit forms a closed loop.
Is it hard to design a circuit?
Simple circuits are relatively easy to design. You allow a high tolerance for the unexpected and accept that there will be failure. But to design something that is very complex, highly reliable, high speed, operate to tight tolerances and has to be protected against all interference is difficult.
How do you diagram a circuit?
So if we were to draw the simple circuit. Using the symbols then how would we do it just draw the
What is Kirchhoff's 1st and 2nd law?
Kirchhoff's first law is based on the conservation of charge because sum of current entering to the junction is equal to sum of current leaving the junction. Kirchhoff's second law states that the algebraic sum of potential drops in a closed circuit is zero. So, it is based on the conservation of energy.
What is Kirchhoff's law formula?
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of all currents leaving a node in any electrical network is always equal to zero. It is based on the principle of conservation of electric charge. The law is also referred to as Kirchhoff's first law. In formula form this is given by: n∑i=1Ii=0.
Why is Kirchhoff's law used?
Kirchhoff's laws are used to help us understand how current and voltage work within a circuit. They can also be used to analyze complex circuits that can't be reduced to one equivalent resistance using what you already know about series and parallel resistors.
What are the 4 important parts to a circuit?
Some basic circuit components which are used in an electronic system is given below.
- Cell. A cell is a device used to power electrical circuits.
- Switch. A switch is a device that can break an electrical circuit by diverting the current from one conductor to another conductor or an insulator. ...
- Light Bulb. ...
- Connecting Wires.
What are the types of circuit?
Types of Electric Circuit- Closed circuits, open circuits, short circuits, series circuits, and parallel circuits are the five main types of electric circuits.







Post a Comment for "Circuit Theory"